Arteriogram
Arteriogram or arteriography involves injection of contrast material into one of the arteries so as to get X ray image of the blood vessel to determine narrowing of arteries. An arteriogram is also called an angiogram.This diagnostic test is used to detect vascular conditions like aneurysm, stenosis or blockage.
Angiograms can be specific to the blood vessels that are being examined, such as cerebral Angiography, renal angiography, aortography or Cardiac Catheterization. Coronary Angiogram or Catheter Angiogram is a minimally invasive procedure where a catheter is inserted into one of the arteries or veins. An IV line is inserted into a blood vessel of either the arm, neck or chest. A catheter is inserted though the IV and contrast material is injected into the desired vein or artery that has to be viewed. A series of x-rays are taken. The contrast material in the blood vessels causes them to appear opaque on an x-ray. There is a small risk of arteriogram leading to blood clots or bleeding and infection at the IV site.
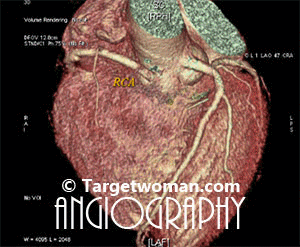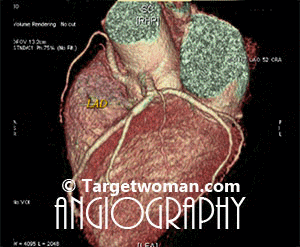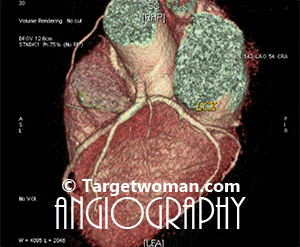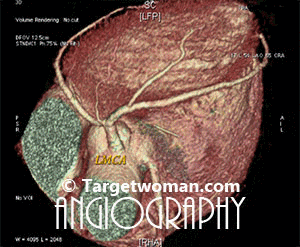
Non invasive 64 slice CT (Computed Tomography) Angiogram (64 MSCTA) can identify the presence of early atherosclerotic plaque deposition before it shows up in the conventional catheter angiogram. Multi slice CT Angiogram can differentiate between various types of plaques - calcified, soft or mixed type. CTA of the multi slice scanners allows faster and comprehensive assessment of arterial blocks and is an important tool in the evaluation of stroke patients - as it enables effective diagnosis of cervicocranial vascular pathologies such as carotid artery stenosis. A 64 slice CT scan images may be pieced together to reveal 3 D images for extracting additional information.
Pulmonary Embolism
When an artery in the lungs gets blocked, it is referred to as a medical condition of Pulmonary embolism. This condition can be life threatening. Often deep vein thrombosis (DVT) can lead to pulmonary embolism. The blood clots may originate in any other part of the body such as the arm, pelvis or legs. These clots travel through the bloodstream and enter the pulmonary arteries. Recent surgery or injury can lead to a blood clots. Persons with heart disease or those on estrogen therapy are at increased risk of pulmonary embolism. Typical symptoms experienced by those suffering from pulmonary embolism are chest pain, sudden shortness of breath and rapid heartbeat. A patient might have wheezing and weak pulse. The symptoms of pulmonary embolism depend on the extent and size of clots. Embolus can also be the result of fat from the bone marrow that has escaped into the bloodstream. It can also occur due to air bubbles formed during intravenous infusion or surgery. While large emboli cause considerable distress such as chest pain, smaller ones cause shortness of breath. Patients suffering from pulmonary embolism tend to have cough that produces sputum. There may be bluish discoloration on the skin and pain in the legs. Fainting spells or seizures might occur due to sudden decrease in oxygen-rich blood to the brain and other organs. Bluish tint on the skin (cyanosis) is observed when one or more large pulmonary arteries are obstructed.
Diagnostic procedures to detect pulmonary embolism:
- Chest X-ray helps in identifying any lung infections
- CAT scan
- ECG
- Perfusion Scan of the lung - This test helps in outlining the blood flow to the lungs and helps in detecting any obstructions.
- V/Q scan involves a a nuclear ventilation-perfusion study of the lungs.
- Pulmonary angiogram involves injection of a special dye into the pulmonary arteries to detect obstructive clots.
- D-dimer test is a test that spots d-dimer molecules released by the clots.
One of the initial steps to help a person suffering from pulmonary embolism is administration of oxygen and analgesics. Oxygen is administered through a nasal cannulae or face mask. Blood clots are treated with anticoagulant drugs like heparin or warfarin. But the duration and dosage of anticoagulants needs to be monitored so that it does not result in bleeding in other body organs. Thrombolysis is a procedure whereby Thrombolytic agents (clot-dissolving agents) are injected into the bloodstream to dissolve existing blood clots. Surgery (Pulmonary embolectomy) is often resorted to for removal of clots.
Transient Ischemic Attack
Transient Ischemic Attack or TIA occurs when there is a brief impairment in blood flow to the brain. This results in stroke-like symptoms such as dizziness, confusion, clumsiness, lack of coordination and difficulty in reading, writing or recognizing people. The patient might experience trouble speaking and understanding speech. There might be slurred speech and dimming of vision. A TIA is different from a stroke in that it does not cause death of brain tissue. Besides, the blockage dissolves soon.
Typical reasons for a transient ischemic attack are blood clots, high blood pressure, diabetes, atrial fibrillation and high cholesterol. Several tests can help diagnose if a person has suffered a transient ischemic attack. Irregular blood flow can be detected by an abnormal sound (bruit) that is noticed with a stethoscope. ECG or angiogram is done to check where the blood flow is blocked. Blood pressure is likely to be very high. The source of atherosclerosis is usually identified with an ultrasound. Aspirin might be prescribed to reduce blood clotting. Other conditions such as hypertension, diabetes and cholesterol need to be treated.
Tags: #Arteriogram #Pulmonary Embolism #Transient Ischemic AttackAt TargetWoman, every page you read is crafted by a team of highly qualified experts — not generated by artificial intelligence. We believe in thoughtful, human-written content backed by research, insight, and empathy. Our use of AI is limited to semantic understanding, helping us better connect ideas, organize knowledge, and enhance user experience — never to replace the human voice that defines our work. Our Natural Language Navigational engine knows that words form only the outer superficial layer. The real meaning of the words are deduced from the collection of words, their proximity to each other and the context.
Diseases, Symptoms, Tests and Treatment arranged in alphabetical order:

A B C D E F G H I J K L M N O P Q R S T U V W X Y Z
Bibliography / Reference
Collection of Pages - Last revised Date: March 7, 2026



