Arteriogram
Arteriogram or arteriography involves injection of contrast material into one of the arteries so as to get X ray image of the blood vessel to determine narrowing of arteries. An arteriogram is also called an angiogram.This diagnostic test is used to detect vascular conditions like aneurysm, stenosis or blockage.
Angiograms can be specific to the blood vessels that are being examined, such as cerebral Angiography, renal angiography, aortography or Cardiac Catheterization. Coronary Angiogram or Catheter Angiogram is a minimally invasive procedure where a catheter is inserted into one of the arteries or veins. An IV line is inserted into a blood vessel of either the arm, neck or chest. A catheter is inserted though the IV and contrast material is injected into the desired vein or artery that has to be viewed. A series of x-rays are taken. The contrast material in the blood vessels causes them to appear opaque on an x-ray. There is a small risk of arteriogram leading to blood clots or bleeding and infection at the IV site.
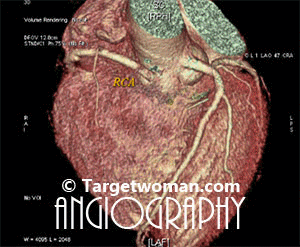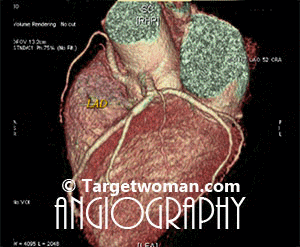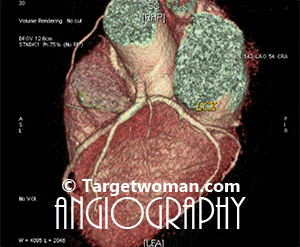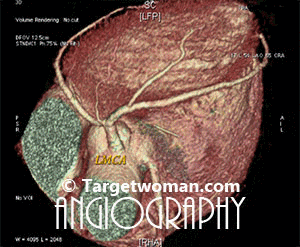
Non invasive 64 slice CT (Computed Tomography) Angiogram (64 MSCTA) can identify the presence of early atherosclerotic plaque deposition before it shows up in the conventional catheter angiogram. Multi slice CT Angiogram can differentiate between various types of plaques - calcified, soft or mixed type. CTA of the multi slice scanners allows faster and comprehensive assessment of arterial blocks and is an important tool in the evaluation of stroke patients - as it enables effective diagnosis of cervicocranial vascular pathologies such as carotid artery stenosis. A 64 slice CT scan images may be pieced together to reveal 3 D images for extracting additional information.
Plethysmography
Plethysmograph is a diagnostic tool that is used to measure flow or pressure. Body plethysmography test involves sitting inside an airtight box and breathing to a particular volume. Blood pressure cuffs are placed around your arm and leg. The patient undergoing plethysmography test must remove clothing on arm and leg and refrain from smoking at least half hour prior to the test. The consequent expansion and decompression of the chest volume allows physicians to rule out any blockages in the limbs as it measures systolic blood pressure. Any abnormal readings can be indicative of arterial occlusive disease, vascular disease or blood clots or even deep venous thrombosis. This test is also referred to as arterial plethysmography and is a vital pulmonary function test. Plethysmography is often used to determine bronchial reactions to histamine or metacholine. But this test is not as accurate as arteriography.
Pelvic Fracture
Fractures of the pelvis account only for about 0.3-6% of all fractures. A pelvic fracture can simply be described as a break in one or more bones comprising the pelvis. Pelvic fracture is a serious condition and requires immediate medical intervention.
- The worst pelvic fractures are caused by high-speed accidents such as car accidents or motorcycle accidents or falls from high places, which have major impact on the body. The greater the force, the more severe the fracture. Depending upon the direction and degree of the force, these injuries can be life threatening.
- Other injuries such as broken bones or damage to liver, kidneys or other organs.
- Pelvic fracture also occurs in people with osteoporosis.
- Pelvic fracture occurs among teens, involved in sports and athletic activities such as football, hockey, skiing and long distance running. These fractures occur with sudden muscle contractions.
- Pelvic fracture is usually caused by falls in elderly people, especially when getting out of a bathtub or descending stairs.
Symptoms of pelvic fracture include severe pain in the groin, hip or lower back area. The pain is bound to worsen when moving the legs. There may be pain in the abdomen and numbness and tingling sensation in the groin or legs. Bleeding from the vagina, urethra or rectum is often noticed with pelvic fractures. There may be difficulty in urinating and difficulty in walking or standing.
Types of Pelvic fractures
Stable or unstable pelvic fractures: In stable pelvic fracture, there is minimal hemorrhage. The break occurs in one point in the pelvic ring. In unstable pelvic fracture, the pelvis becomes unstable. The break occurs in two or more break points in the pelvic ring. There occurs moderate to severe hemorrhage.
Open or closed pelvic fractures: If open skin wound occurs during the fracture in the lower abdomen, it is called open pelvic fracture. If no skin wounds occur, then it is closed pelvic fracture.
Diagnostic tests such as x-rays, CT scans are used to diagnose pelvic fractures. MRI allow a detailed picture of the pelvic area. Abdominal ultrasound is used to find internal bleeding and other injuries within the abdomen. Urethrography may be conducted to check injuries in urethra by means of an injected dye. Arteriography, in which dye is injected in the arteries to check for internal bleeding within the pelvis, is sometimes used.
Treatment to the pelvic fracture depends upon the severity of the injury caused. A pelvic fracture is a serious injury. In some cases, it may be complicated with injuries in other parts of the body and severe shock as well. Sometimes severe internal and external bleeding and damage to the internal organs could occur. In these situations, immediate attempt is made by the emergency doctor to stop internal and external bleeding caused by the injury. In case of minor fracture, the treatment would merely consist of bed rest and painkillers.
Most of the times, surgery is undertaken to repair the pelvic fracture. Healing after surgery can take anywhere between few weeks to several months. Thus a lengthy rehabilitation becomes necessary after an extensive pelvic surgery.
At TargetWoman, every page you read is crafted by a team of highly qualified experts — not generated by artificial intelligence. We believe in thoughtful, human-written content backed by research, insight, and empathy. Our use of AI is limited to semantic understanding, helping us better connect ideas, organize knowledge, and enhance user experience — never to replace the human voice that defines our work. Our Natural Language Navigational engine knows that words form only the outer superficial layer. The real meaning of the words are deduced from the collection of words, their proximity to each other and the context.
Diseases, Symptoms, Tests and Treatment arranged in alphabetical order:

A B C D E F G H I J K L M N O P Q R S T U V W X Y Z
Bibliography / Reference
Collection of Pages - Last revised Date: March 7, 2026



