Cerebral hemorrhage
Cerebral hemorrhage also known as stroke is associated with ischemic conditions. These types of conditions often occur when the brain experiences shortage of blood supply. The brain cells get damaged as a result of bleeding internally. There are several types of cerebral hemorrhage caused in different regions of the brain. The most predominant type of cerebral hemorrhages include:
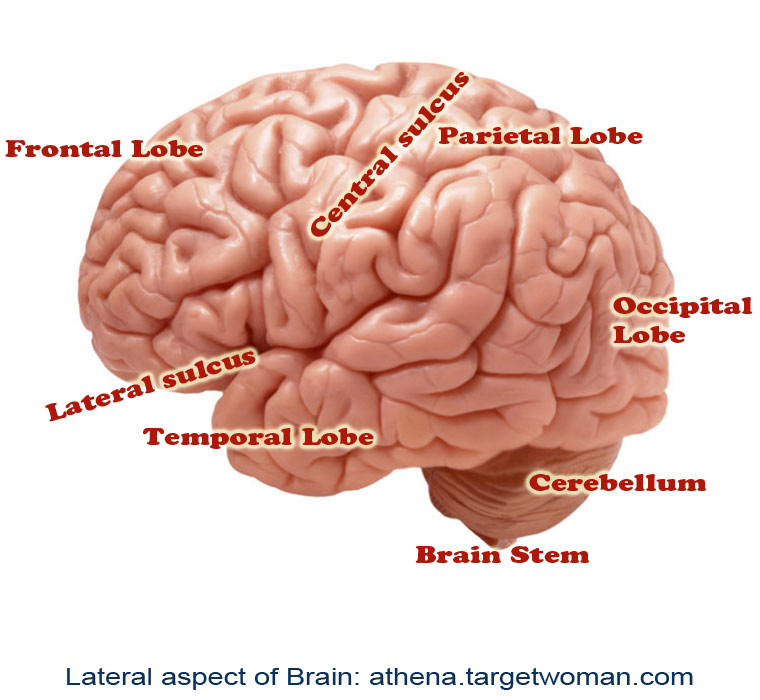
Intra cerebral hemorrhages: In this condition the brain experiences internal bleeding and it occurs in the region of the cerebellum depending upon the zone of injury that leads to the bleeding. The parenchymal tissues of the brain undergo severe damage in this condition.
Subarachnoid hemorrhages: This type of bleeding is caused between the membranes lining the brain.
Subdural hematoma: This is commonly found in athletes such as boxers and wrestlers. The injury or trauma is caused to the veins underneath the dura of the brain.
Epidural hematoma: This is also a condition caused because of trauma or head injury. The meningeal artery is ruptured leading to bleeding in the region between skull and membrane covering the brain.
Other forms of damage caused to the brain predominantly include ventricular damage which is caused because of trauma to the ventricles of the brain which contain the cerebrospinal fluid.
Causes of stroke
Cerebral hemorrhage or stroke may occur because of many reasons. In most forms it is closely associated with congenital abnormalities of the brain and also because of trauma or altered lifestyle patterns. Some of the common conditions that cause cerebral hemorrhages are aneurysms; deformities in the arterial and venous supply to the brain, presence of abnormal proteins such amyloids which lead to deterioration of brain cells and hypertension.
Symptoms
The major risk factors for cerebral hemorrhage are hypertension, trauma and alcoholism. This condition mostly occurs in patients who have a history of diabetes, habits such as alcoholism, smoking and aged people. Many patients experience numbness in their hands, legs, blurred vision, headaches, confusion and also impaired speech patterns because of hypertension associated cerebral hemorrhage. The damage is caused predominantly in the ventricular region of the brain.
The symptoms associated with cerebral hemorrhage often lead to paralysis, seizures and sudden loss of consciousness, tingling sensation in the feet, altered taste patterns, nausea and inability to swallow. This happens because of ischemia or lack of blood supply to the brain which inevitably affects the neuromuscular activity of the body. In addition to these, cerebral hemorrhage also results due to liver damage or brain tumor.
Diagnosis
In case of head injury or trauma, the hematomas have to be removed as soon as possible with thorough evaluation of the damaged regions of the skull in association with the membranes to rule out all possibilities of internal organ bleeding or presence of any kind of blood clots. Patients are rushed in for radiological examinations to minimize the time required to intervene the situation of head injury as any delay can be fatal. In patients with hypertension and previous history of diabetes, thorough radiological examination is performed to identify the ischemic regions present in the brain. Abnormal blood vessels are corrected using interventional radiology.
Treatment options for cerebral hemorrhages are often associated with treatments pertaining to hypertension and diabetes. Patients are counseled to undergo corrective surgeries in case of hemorrhages associated with aneurysms.
Cerebral aneurysm
Cerebral aneurysm occurs when a weakness in the blood vessel of the brain causes it to bulge. This can be congenital or caused due to injury. A few cerebral aneurysms might rupture especially in cases of hypertension. A person suffering cerebral aneursym might suffer loss of vision, double vision and headaches. There might be increased intracranial pressure and swelling of the optic nerve. Brain MRI or CAT are taken to ascertain presence and location and size of Cerebral aneurysm. Spinal tap might be done.
Silent Stroke
When a person suffers a stroke that is not characterized by any outward symptoms, it is a silent stroke. Often even the patient is not aware of it. A silent stroke usually affects those areas of the brain that deal with thought process and mood regulation. A silent stroke damages a few cells in the brain, which are likely to die over time. A link between depression and silent stroke has been noticed. They are both indicative of reduced blood supply to the brain.
A silent stroke can cause damage to the brain and can be a precursor to a major stroke or transient ischemic attack. Hypertension, atrial fibrillation and smoking are the major triggers for a silent stroke. Elevated levels of total homocysteine or acrolein is a risk factor for a silent stroke. Untreated diabetes can also lead to a silent stroke. A silent stroke episode is usually detected through an MRI can it usually causes lesions that are visible during imaging.
A silent stroke can occur in different ways:
Ischemic stroke: This kind of stroke is the one that most patients suffer when there is blockage of blood supply to the brain due to impaired blood vessels.
Hemorrhagic stroke: This kind of stroke occurs when a blood vessel carrying blood to the brain gets weak and ruptures. Aneurysms are examples of a condition leading to a stroke.
Studies have proved that persons engaging in moderate or intensive exercise on a regular basis had far lesser chance of experiencing a silent stroke.
At TargetWoman, every page you read is crafted by a team of highly qualified experts — not generated by artificial intelligence. We believe in thoughtful, human-written content backed by research, insight, and empathy. Our use of AI is limited to semantic understanding, helping us better connect ideas, organize knowledge, and enhance user experience — never to replace the human voice that defines our work. Our Natural Language Navigational engine knows that words form only the outer superficial layer. The real meaning of the words are deduced from the collection of words, their proximity to each other and the context.
Diseases, Symptoms, Tests and Treatment arranged in alphabetical order:

A B C D E F G H I J K L M N O P Q R S T U V W X Y Z
Bibliography / Reference
Collection of Pages - Last revised Date: February 23, 2026



