Cerebral hemorrhage
Cerebral hemorrhage also known as stroke is associated with ischemic conditions. These types of conditions often occur when the brain experiences shortage of blood supply. The brain cells get damaged as a result of bleeding internally. There are several types of cerebral hemorrhage caused in different regions of the brain. The most predominant type of cerebral hemorrhages include:
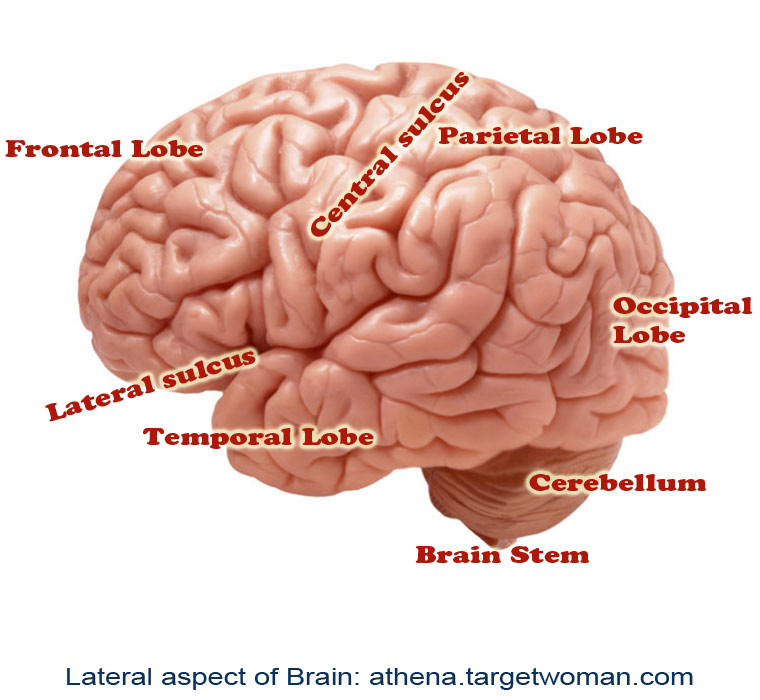
Intra cerebral hemorrhages: In this condition the brain experiences internal bleeding and it occurs in the region of the cerebellum depending upon the zone of injury that leads to the bleeding. The parenchymal tissues of the brain undergo severe damage in this condition.
Subarachnoid hemorrhages: This type of bleeding is caused between the membranes lining the brain.
Subdural hematoma: This is commonly found in athletes such as boxers and wrestlers. The injury or trauma is caused to the veins underneath the dura of the brain.
Epidural hematoma: This is also a condition caused because of trauma or head injury. The meningeal artery is ruptured leading to bleeding in the region between skull and membrane covering the brain.
Other forms of damage caused to the brain predominantly include ventricular damage which is caused because of trauma to the ventricles of the brain which contain the cerebrospinal fluid.
Causes of stroke
Cerebral hemorrhage or stroke may occur because of many reasons. In most forms it is closely associated with congenital abnormalities of the brain and also because of trauma or altered lifestyle patterns. Some of the common conditions that cause cerebral hemorrhages are aneurysms; deformities in the arterial and venous supply to the brain, presence of abnormal proteins such amyloids which lead to deterioration of brain cells and hypertension.
Symptoms
The major risk factors for cerebral hemorrhage are hypertension, trauma and alcoholism. This condition mostly occurs in patients who have a history of diabetes, habits such as alcoholism, smoking and aged people. Many patients experience numbness in their hands, legs, blurred vision, headaches, confusion and also impaired speech patterns because of hypertension associated cerebral hemorrhage. The damage is caused predominantly in the ventricular region of the brain.
The symptoms associated with cerebral hemorrhage often lead to paralysis, seizures and sudden loss of consciousness, tingling sensation in the feet, altered taste patterns, nausea and inability to swallow. This happens because of ischemia or lack of blood supply to the brain which inevitably affects the neuromuscular activity of the body. In addition to these, cerebral hemorrhage also results due to liver damage or brain tumor.
Diagnosis
In case of head injury or trauma, the hematomas have to be removed as soon as possible with thorough evaluation of the damaged regions of the skull in association with the membranes to rule out all possibilities of internal organ bleeding or presence of any kind of blood clots. Patients are rushed in for radiological examinations to minimize the time required to intervene the situation of head injury as any delay can be fatal. In patients with hypertension and previous history of diabetes, thorough radiological examination is performed to identify the ischemic regions present in the brain. Abnormal blood vessels are corrected using interventional radiology.
Treatment options for cerebral hemorrhages are often associated with treatments pertaining to hypertension and diabetes. Patients are counseled to undergo corrective surgeries in case of hemorrhages associated with aneurysms.
Hemorrhage
Hemorrhage refers to loss of blood from a person. Internal Hemorrhage happens when blood vessels rupture and lead to blood leakage. External Hemorrhage is a situation where a person loses copious amount of blood externally. This can happen from a natural body orifice or through a cut in the skin.
Hemorrhage locations
Hematuria: Loss of blood in the urine.
Hematemesis: Loss of blood in vomit.
Brain hemorrhage: Bleeding in the skull, brain tissue or rupture within the blood vessels in the head.
Gynecological hemorrhage: Bleeding through the vagina or ovaries.
A person can also experience upper gastrointestinal bleeding, pulmonary hemorrhage or rectal hemorrhage. Hemorrhage can occur due to high blood pressure, blood clotting disorders, uncontrolled diabetes or leukemia.
Bleeding in the Eye
Bleeding in the eyes is associated with many underlying conditions like hyphema, blood vessel damage (subconjuctival hemorrhage), diabetic retinopathy and vitreous hemorrhage.
The conditions for diabetic retinopathy occur because of long term diabetics. Prolonged high blood sugar levels can damage the blood vessels associated with the retina of the eye. These blood vessels become leaky or clogged. The leaky blood vessels initiate the process of hemorrhages which are visualized as spots of bleeding. In some instances the clogged blood vessels obstruct the supply of oxygen to the retina causing ischemic condition. Maintaining proper blood sugar levels along with controlled pressure is essential.
Subconjuctival hemorrhage occurs due to damage caused to the sclera or the white portion of the eye. The blood released because of the damaged blood vessel is trapped under the conjunctiva. Subconjuctival hemorrhage associated eye bleeding is often painless. It is mainly caused because of high blood pressure and also triggered by cough, vomiting and sneezing. The blood spots disappear gradually. Medical attention is required if symptoms such as blurred vision, pain and recurrent hemorrhages occur. The choice of medication given for subconjunctival hemorrhage are blood thinners like heparin and Coumadin.
Hyphema is caused due to injury to the eye. The trauma caused in the eye can be of blunt or closed types depending upon the intensity of the damage. Most of these traumas which result in the bleeding of the eye are because of external sources such sharp objects, industrial chemicals, fumes, injuries associated with boxing and martial arts. Smaller hyphemas are associated with bleeding and swelling of the eye and extreme hyphemas are associated with pain, bleeding, swelling and reddening of the entire eye. The diagnosis for hyphema is usually performed by an ophthalmologist evaluating the entire history of the case followed by series of visual acuity tests. A CT scan is also recommended if there is a suspicion of bone damage in the eye region caused because of trauma.
Vitreous hemorrhage is another predominant cause for eye bleeding. Other factors include tumors adjacent to the vitreous humor of the eye and macro aneurysms. The treatment options for vitreous hemorrhages include vitrectomy and through Krypton laser therapy.
Rare causes for bleeding in the eye
Apart from the common factors that are associated with the hemorrhages caused in the eye, some rare conditions such cancers and iritis also cause bleeding in the eyes. Cancers of the eye are usually diagnosed by biopsy and also by careful visual examination. Since the symptoms of the bleeding eye disease may mask the diagnosis of underlying cancer or tumor, malignancy is confirmed by pathologic determination. Iritis is caused because of the inflammation in the iris of the eye. It may be the result of a trauma caused to the eye or underlying systemic conditions such as sarcoidosis and tuberculosis. Analgesics are recommended for common iritis. Patients are advised to wear dark sunglasses.
At TargetWoman, every page you read is crafted by a team of highly qualified experts — not generated by artificial intelligence. We believe in thoughtful, human-written content backed by research, insight, and empathy. Our use of AI is limited to semantic understanding, helping us better connect ideas, organize knowledge, and enhance user experience — never to replace the human voice that defines our work. Our Natural Language Navigational engine knows that words form only the outer superficial layer. The real meaning of the words are deduced from the collection of words, their proximity to each other and the context.
Diseases, Symptoms, Tests and Treatment arranged in alphabetical order:

A B C D E F G H I J K L M N O P Q R S T U V W X Y Z
Bibliography / Reference
Collection of Pages - Last revised Date: February 23, 2026



