Tourette's Syndrome
Gilles de la Tourette syndrome is a neurological disorder that involves uncontrollable repetitive movements or abnormal sounds called tics. These tics are rapid movements such as blinking, shrugging the shoulders, or jerking an arm or sounds like humming, clearing the throat, grunting, or yelling out a word or phrase. Tics involved with movement are called motor tics and tics involving sound are called vocal tics. There is no specific cause that results in Tourette's syndrome. It could be either due to inherited gene disorder or certain chemical imbalance in the brain.
People with Tourette's syndrome are not able to control themselves from tics. The condition typically starts in childhood between the ages of 2 and 12. A male child is more likely to develop Tourette's syndrome than a girl child. Tourette's syndrome occurs in people from all ethnic groups. It stays with the person for life. However symptoms are at their peak during the early teens and gradually improve during adulthood. Motor and vocal tics are intensified with fear, stress, apathy, fatigue or excitement. Tics are normally under control when the affected person is asleep.
Simple and complex tics
Tourette's syndrome almost always starts with motor tics and the affected person slowly develops vocal tips too in due course. The symptoms of Tourette's syndrome may range from simple tics to complex ones. Simple motor tics may include only few muscle groups such as eye-blinking, facial grimacing, nose-twitching, head-jerking. Complex tics involve many muscle groups. Complex ones include jumping, touching other people or things or it can even be an extreme tic.
Throat clearing, yelping, sniffing, hissing, barking, coughing and tongue clicking are some of the simple vocal tics while complex vocal tics include uttering words or phrases out of context, Coprolalia (obscene gestures), and echolalia (repeating a sound, word, or phrase just heard).
Treatment
There is no cure for Tourette's syndrome. No intervention is required when the tics are simple and do not affect daily activity. However the affected person as well as the people around him need to be educated about Tourette's syndrome so as to avoid weird reactions. Severe tics may be treated with medication and behavioral therapies. However medications do not help in suppressing the tics completely. Neuroleptics and alpha-adrenergic agonists have been effective in treating severe tics. These medications may lead to certain side effects.
Deep Brain Stimulation
Deep brain stimulation is a specialized neurosurgical treatment option for patients suffering from a special group of neurological disorders called 'Movement Disorders'. Deep Brain Stimulation or DBS is an advanced procedure performed by neurosurgeons for treating patients who cannot achieve optimal results through conventional medical therapy alone.
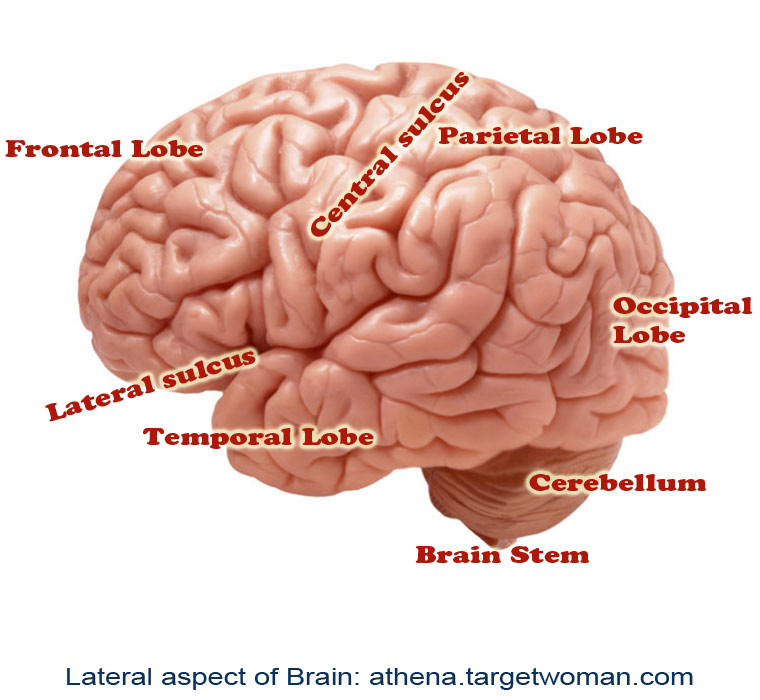
Neurophysiology of Movement Disorders
Movement disorders refer to conditions associated with changes in specific areas of the nervous system which results in abnormal involuntary movements, slow or reduced movements. The two main areas of the brain which are affected in movement disorders are the basal ganglia and the sub-thalamic nucleus. The disorders are classified into various groups such as hypokinetic disorders (e.g.: Parkinsons), hyperkinetic disorders (e.g.: Huntington's disease), and Non-motor disorders (e.g.: Tourette's Syndrome and Obsessive Compulsive Disorders). When these nuclei start having abnormal electrical activity (discharging too much or too little), the patient experiences specific symptoms related to movement.
Indications for Deep Brain Stimulation
Deep brain stimulation is used for patients who usually suffer from movement disorders such as Parkinsons, tremors, and dystonia. It is called Deep Brain Stimulation because surgically placed electrodes are used to stimulate specific areas (nuclei) deep inside the brain. The most common nuclei commonly stimulated are the Globus Pallidus and the sub-thalamic nuclei.
The idea behind DBS is that it functions somewhat like a 'pacemaker' in the brain, periodically sending electrical signals to the specific nuclei, thereby modulating the effect of these nuclei. Hence, DBS is also called as neuromodulation therapy'. In DBS, specific electrical signals are sent to the abnormally functioning nuclei to reduce or increase their activity.
Components
There are three components of the Deep Brain Stimulation system. They are:
The Stimulating Electrodes
The IPG – Internal Pulse Generator (the pacemaker)
The Extension - connecting leads between the Electrode and IPG.
The IPD contains a battery pack which has to be replaced every 4 years. The IPG is programmed by the neurologist based on the specific disease condition of the patient, and the placement of DBS requires regular follow-ups for programming the IPG based on the disease condition, if needed.
Procedure
Specialized Brain Mapping technology is used to locate the specific nuclei which are suspected to be abnormally functioning. These nuclei are the 'target area' for DBS. A specially designed stereotaxic frame is attached to the patient's head which provides a three-dimensional reference system for the patient's brain and enables the neurosurgeon to precisely locate the nuclei or track the electrode tip during placement.
The procedure normally takes up to three hours and is performed by a neurosurgeon specially trained in the procedure. The surgery is called awake craniotomy since the patient is awake during the entire duration of the procedure so that his neurological functions can be assessed in real-time to see the 'before and after' results due to the electrode placement. Following the placement of the electrodes, the IPGs are implanted either during the time of the surgery or later on. Each brain is unique, and hence the IPGs have to be specially programmed and the settings have to be specific for each patient. This is usually done about 2 weeks after the electrode placement.
Clinical Results
It is not exactly known how DBS functions, but there have been marked clinical improvements for patients with Parkinson's disease, tremors, and dystonia. Although a large percentage of patients report significant improvement after DBS surgery, there is no guarantee that DBS will help every patient with movement disorder.
Patients with Parkinson's report 60-80% improvement in tremor and slowness of movement. Patients on an average report 50% improvement in their walking and balance following DBS. Others with dyskinesia (involuntary movements) report more than 80% improvement following DBS.
Complications
Although DBS on the whole has proven safe and effective, there is a possible 2-3% risk of intra-cranial hemorrhage and meningitis due to leakage of cerebro-spinal fluid. There is a 15% chance of developing infection due to the placement of the electrodes. There is a possibility that seizures may occur, if the tip of the electrode migrates, thereby stimulating other areas of the brain. However such findings have not been reported until now.
Future of DBS
Besides movement disorders, DBS has been used to chronic pain, and currently possibilities of using DBS for other cognitive disorders such as severe depression, obsessive compulsive disorder, eating behavioral disorders and drug addiction, are underway.
Urine Amino Acid Analysis
Amino acids play a vital role as building blocks of proteins and also as intermediates in metabolism. These amino acids help in neurotransmitter function, pH balance regulation, hormone metabolism, pain and inflammation control, detoxification, cholesterol metabolism and various other biological activities. Excess or deficiency of amino acids in the body either due to dietary restriction or inherited metabolic problems can cause very serious health issues.
Urine amino acid test measures the amino acid levels in the urine. It is a medical test that helps in identifying underlying chronic disorders caused by amino acid imbalances and vitamin and mineral deficiencies. Most often, Amino acid test is performed as a screening test in newborn and children to address metabolism disorders. If any of the essential amino acids are not available in sufficient quantities, the production of protein is compromised with inefficient metabolism. The deficiency may cause disorders such as ADD, depression, Tourette syndrome, tic disorder, OCD, seizures and others.
Urine amino acid test provides valuable information on amino acid imbalance in the body by identifying:
Dietary protein adequacy
Gastrointestinal dysfunction
Enzyme functionality
Protein intolerance
Vitamin and mineral deficiencies
Renal and hepatic dysfunction, psychiatric abnormalities
Susceptibility to degenerative disorders
Inflammatory response and oxidative stress
Reduced detoxification capacity and many other inherent and acquired disorders
There are around 20 different amino acids in the urine. If the urine indicates any one or two of the amino acid levels as higher than normal, the person may have an inherent error of metabolism. Diagnosing it during infancy can prevent problems such as brain damage.
No prior preparation is required for the test. Clean catch urine sample is collected to perform the test. Few laboratories ask for first morning urine and few other prefer 24-hour urine test for assessing the amino acid levels. 24 hour urine test gives a detailed picture of highs and lows of various amino acid levels through the day, whereas first morning urine identifies current amino acid status and any existing imbalances. Reports are presented in a tabular format grouped into functional categories clearly indicating:
- Amino acids levels (both essential and non essential)
- Gastrointestinal markers
- Detoxification markers
- Neurological markers
- Magnesium dependent markers
- Urea cycle metabolites
- B12, B6, folate dependent markers
Urine amino acid analysis in itself cannot be used as the ultimate diagnostic tool and it is normally supported by specific and further testing to confirm genetic and metabolic disorders. However, test reports will help in identifying the exact deficiencies that are contributing to disorders and allow for the precise replacement of those amino acids. The report will help nutritionists to draw a right supplement plan to replenish the required amino acids in the body.
Tags: #Tourette's Syndrome #Deep Brain Stimulation #Urine Amino Acid Analysis
At TargetWoman, every page you read is crafted by a team of highly qualified experts — not generated by artificial intelligence. We believe in thoughtful, human-written content backed by research, insight, and empathy. Our use of AI is limited to semantic understanding, helping us better connect ideas, organize knowledge, and enhance user experience — never to replace the human voice that defines our work. Our Natural Language Navigational engine knows that words form only the outer superficial layer. The real meaning of the words are deduced from the collection of words, their proximity to each other and the context.
Diseases, Symptoms, Tests and Treatment arranged in alphabetical order:

A B C D E F G H I J K L M N O P Q R S T U V W X Y Z
Bibliography / Reference
Collection of Pages - Last revised Date: December 30, 2025



