Hypoxia
The body needs a specific amount of Oxygen to function normally and when this amount is lowered the body experiences hypoxia. Hypoxia literally means lack of oxygen for effective ventilation.
Hypoxemia refers to a state of abnormally low level of Oxygen in the blood.
Anoxia refers to the condition of absence of Oxygen supply to an organ or tissue
Anoxemia refers to the condition where the blood stream contains below normal amount of Oxygen.
Hypoxia is primarily classified into:
Generalized hypoxia: affects the entire body, may occur in normal healthy people when they scale high altitudes.
Local hypoxia: affects one particular region of the body.
When the level of oxygen in the blood reduces, it leads to the condition. People suffering from conditions like ischemia or blockage/constriction of blood vessels may suffer from hypoxia. In general when people travel from low to high altitudes, they may face this problem as the oxygen level depletes with altitude.
Hypoxia causes
Any condition wherein the body is deprived of oxygen can lead to hypoxia. Major causes that lead to the condition include:
- Severe head trauma
- Ischemia
- Asthma Severe Asthma can result in hypoxia and in Hypercarbia or Hypercapnia (elevated levels of Carbon dioxide CO2 in blood)
- Pulmonary embolism
- Carbon monoxide poisoning
- Chronic alveolar hypo ventilation
- Shock can result in cellular hypoxia in the extremities
- Suffocation
- Choking
- High altitude climbing
- Inadequate ventilation
Types of hypoxia
Hypemic hypoxia: Obstruction in the ability of the blood to deliver oxygen, caused by carbon monoxide poisoning.
Anemic Anoxia: Occurs due to a decrease in the hemoglobin or RBC making it too little for the blood to carry oxygen. Anemia may be the result of iron deficiency, hemorrhage or shortened life span of RBC owing to an autoimmune disease.
Histotoxic: When the required amount of oxygen reaches the body part, however it does not utilize it because of its reduced ability, it is called as histotoxic hypoxia. Cyanide poisoning, for example, incapacitates a cellular enzyme essential for oxygen utilization. Other causes include: Alcohol, narcotics, acetone, formaldehyde and some anesthetic agents.
Hypoxic: Also called as Hypoxemic Anoxia: When the body does not receive the required amount of oxygen it leads to low partial pressure of oxygen in the blood thus leading to hypoxic hypoxia. The oxygen pressure of the blood which gets supplied to other body tissues is too low to push and flood the hemoglobin with oxygen. High altitude has lower density of air and lower pressure of oxygen than at sea level. Altitude Sickness occurs because the partial pressure of oxygen decreases with altitude. Hypoxemia is the direct result of lower oxygen in the high altitude which translates to lower level oxygen in the blood.
Stagnant: Obstruction of blood that carries oxygen. It can be due to exposure to cold, diseases which stifle blood circulation to the extremities or ergot poisoning.
Pulse Oximetry, a non invasive test is useful to diagnose Hypoxia. A blood test like serum lactate test can show elevated levels of lactic acid - the result of starvation of oxygen in tissues. The normal level of lactic acid is less than 2 mmol/L. However an increase in lactic acid alone does not indicate hypoxia and some form of Anoxia does not increase the lactic acid concentration. Symptoms may be dangerous on the onset and may include the following:
Generalized hypoxia
- Tachypnea or rapid breathing
- Severe headache
- Dizziness
- Nausea
- Tingling sensation
- Visual impairment
- Shortness of breath
- Bluish tint on the lips or on finger tips
- Coma
- Seizures
- Euphoria
- Mental fatigue
- Muscle fatigue
Local hypoxia
- Hot and cold flashes
- Discoloration of skin
- Pain in the area of hypoxia
- Severe hypoxia may cause gangrene
Hypoxia Treatment
Some types of Hypoxia cannot be prevented. Treatment depends on the severity of the condition and the appearance of the clinical symptoms. Treatment may include the following:
- Restoration of the tissue oxygen by supplementing the air supply with 100 % oxygen.
- Blood pressure and heart rate should be brought back to normal.
- In case of high altitudes, the person should be given sufficient rest and should not climb any further.
- Hypoxemic hypoxia patients can be put on blood transfusion.
- Proper medication and timely treatment can help save the life.
Hypertension (High Blood Pressure)
Hypertension is a medical term for abnormally high blood pressure. When the blood pressure readings consistently show elevated readings over a period of time, hypertension is the resultant condition. Normal blood pressures hovers around the range of 120/80 mmHg. Pre-hypertension is a Situation when your blood pressure hovers around 130 for systolic pressure and between 80 and 89 for diastolic pressure. Factors that can affect blood pressure are many - salt content of the body, volume of water in the body and the condition of the kidneys, nervous system and blood vessels.
It is essential not to ignore signs of hypertension - high blood pressure, since it increases the strain on the heart and lead to stroke or heart attack. Secondary hypertension is noticed among 5% of the people. The causes can be linked to kidney disease or adrenal gland disease or even narrowing of the aorta. It is sometimes seen due to use of steroids, contraceptive pills. Hypertension induced by pregnancy or pre-eclampsia is another cause for secondary hypertension among women.
Hypertension is known to run in families and chances of your developing hypertension are high if your close relatives suffer from it. Other causes of hypertension are obesity and excess stress. Those who consume large quantities of alcohol or salt are also at higher risk of getting hypertension.
Symptoms of hypertension
- Crushing chest pain
- Heart failure
- Tiredness and confusions
- Nose bleed
- Irregular heartbeat
Tackling hypertension
If you are obese, it is necessary to lose weight and make dietary changes. Decrease levels of fat and sodium. A modest restriction of salt may decrease blood pressure. Instead increase the proportion of fiber, fruits and vegetables. Limit your alcohol intake to one or two glasses a day. Introduce exercise into your daily routine to treat hypertension. Regular, moderate aerobic exercise can modestly decrease blood pressure and has many other beneficial effects. Gradual weight loss through modified calorie intake and increased physical activity is a good approach to tackle high blood pressure.
Deep Brain Stimulation
Deep brain stimulation is a specialized neurosurgical treatment option for patients suffering from a special group of neurological disorders called 'Movement Disorders'. Deep Brain Stimulation or DBS is an advanced procedure performed by neurosurgeons for treating patients who cannot achieve optimal results through conventional medical therapy alone.
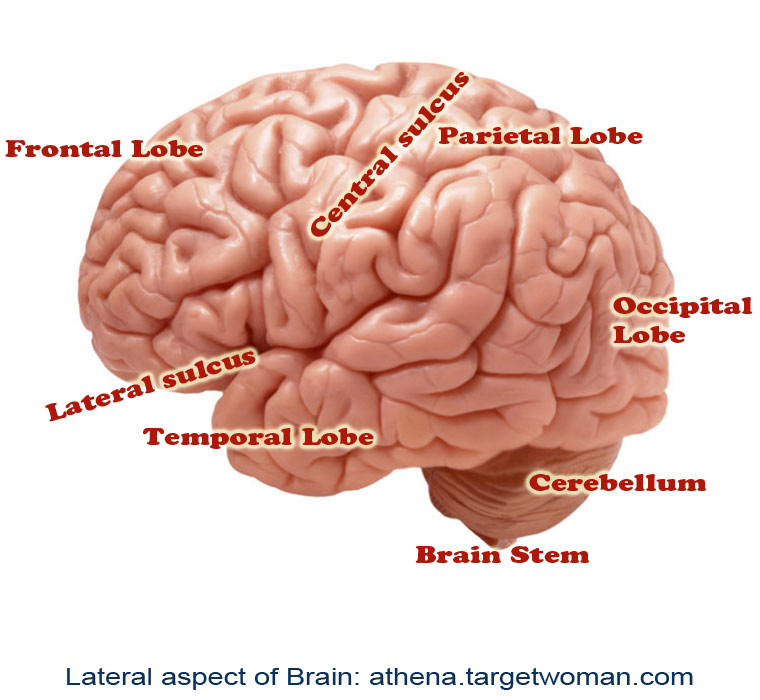
Neurophysiology of Movement Disorders
Movement disorders refer to conditions associated with changes in specific areas of the nervous system which results in abnormal involuntary movements, slow or reduced movements. The two main areas of the brain which are affected in movement disorders are the basal ganglia and the sub-thalamic nucleus. The disorders are classified into various groups such as hypokinetic disorders (e.g.: Parkinsons), hyperkinetic disorders (e.g.: Huntington's disease), and Non-motor disorders (e.g.: Tourette's Syndrome and Obsessive Compulsive Disorders). When these nuclei start having abnormal electrical activity (discharging too much or too little), the patient experiences specific symptoms related to movement.
Indications for Deep Brain Stimulation
Deep brain stimulation is used for patients who usually suffer from movement disorders such as Parkinsons, tremors, and dystonia. It is called Deep Brain Stimulation because surgically placed electrodes are used to stimulate specific areas (nuclei) deep inside the brain. The most common nuclei commonly stimulated are the Globus Pallidus and the sub-thalamic nuclei.
The idea behind DBS is that it functions somewhat like a 'pacemaker' in the brain, periodically sending electrical signals to the specific nuclei, thereby modulating the effect of these nuclei. Hence, DBS is also called as neuromodulation therapy'. In DBS, specific electrical signals are sent to the abnormally functioning nuclei to reduce or increase their activity.
Components
There are three components of the Deep Brain Stimulation system. They are:
The Stimulating Electrodes
The IPG – Internal Pulse Generator (the pacemaker)
The Extension - connecting leads between the Electrode and IPG.
The IPD contains a battery pack which has to be replaced every 4 years. The IPG is programmed by the neurologist based on the specific disease condition of the patient, and the placement of DBS requires regular follow-ups for programming the IPG based on the disease condition, if needed.
Procedure
Specialized Brain Mapping technology is used to locate the specific nuclei which are suspected to be abnormally functioning. These nuclei are the 'target area' for DBS. A specially designed stereotaxic frame is attached to the patient's head which provides a three-dimensional reference system for the patient's brain and enables the neurosurgeon to precisely locate the nuclei or track the electrode tip during placement.
The procedure normally takes up to three hours and is performed by a neurosurgeon specially trained in the procedure. The surgery is called awake craniotomy since the patient is awake during the entire duration of the procedure so that his neurological functions can be assessed in real-time to see the 'before and after' results due to the electrode placement. Following the placement of the electrodes, the IPGs are implanted either during the time of the surgery or later on. Each brain is unique, and hence the IPGs have to be specially programmed and the settings have to be specific for each patient. This is usually done about 2 weeks after the electrode placement.
Clinical Results
It is not exactly known how DBS functions, but there have been marked clinical improvements for patients with Parkinson's disease, tremors, and dystonia. Although a large percentage of patients report significant improvement after DBS surgery, there is no guarantee that DBS will help every patient with movement disorder.
Patients with Parkinson's report 60-80% improvement in tremor and slowness of movement. Patients on an average report 50% improvement in their walking and balance following DBS. Others with dyskinesia (involuntary movements) report more than 80% improvement following DBS.
Complications
Although DBS on the whole has proven safe and effective, there is a possible 2-3% risk of intra-cranial hemorrhage and meningitis due to leakage of cerebro-spinal fluid. There is a 15% chance of developing infection due to the placement of the electrodes. There is a possibility that seizures may occur, if the tip of the electrode migrates, thereby stimulating other areas of the brain. However such findings have not been reported until now.
Future of DBS
Besides movement disorders, DBS has been used to chronic pain, and currently possibilities of using DBS for other cognitive disorders such as severe depression, obsessive compulsive disorder, eating behavioral disorders and drug addiction, are underway.
Enter your health or medical queries in our Artificial Intelligence powered Application here. Our Natural Language Navigational engine knows that words form only the outer superficial layer. The real meaning of the words are deduced from the collection of words, their proximity to each other and the context.
Diseases, Symptoms, Tests and Treatment arranged in alphabetical order:

A B C D E F G H I J K L M N O P Q R S T U V W X Y Z
Bibliography / Reference
Collection of Pages - Last revised Date: July 26, 2024



